Basic HTML Version













12
SECTION 1
12
While reading Text 3, highlight the key-words in order to understand what charges are.
(to) attract
attrarsi
dielectric
dialettico, isolante
paper
carta
repulsion
repulsione
rubber
gomma
TECHNICAL ENGLISH
13
Match the two halves of each definition.
1
a static electric charge is the result of
a
dielectric materials
2
paper and rubber are
b
no motion of electrons and protons
3
in static electricity there is
c
separating electrons and protons
4
electrostatics is
d
the study of static charges
14
Scan the text in order to highlight the sentences useful to solve these easy problems.
a
12.5 x 10
18
electrons are added to a neutral dielectric.
What will its charge be in coulombs?
b
Dielectric has a positive charge of 12.5 x 10
18
protons.
What will its charge be in coulombs?
c
A dielectric with +Q of 2 C has 12.5 x 10
18
electrons added.
What will its charge be now?
Charges
T
o separate electrons and protons you can, for
example, rub
1
a hard
rubber
or a comb on a sheet
of
paper
; if the paper is left free to move, the rubber
will
attract
one corner of the paper. This shows that
rubbing the paper with a rubber has created a static
electric charge. Rubbing has separated the electrons
and the protons and produced a charge of excess
electrons on the surface of the rubber and a charge of
excess protons on the paper.
Because both paper and rubber are insulating
materials (
dielectric
) they retain their extra electrons
or protons and, as a result, the paper and rubber are no
longer neutral, and each has an electric charge. It is
these electric charges that fuel the force of attraction
between the rubber and the paper. This mechanical
force of attraction or
repulsion
between charges
is the fundamental method by which electricity can
be revealed. Any charge is an example of static
electricity because the electrons or protons are not in
motion. There are many examples.
When you walk across a wool rug
2
, your body becomes
charged with excess electrons. Similarly, silk, fur, and
glass can be rubbed to produce a static charge. This
effect is more evident in dry weather because a damp
3
dielectric does not hold its charge so well.
The electrical charge used in many common
applications requires many billions of electrons
and protons. Thus a unit of measurement has been
defined, the coulomb (C), a coulomb is a charge of
6.25 x 10
18
electrons or protons stored in a dielectric.
The study and analysis of static charges and their
forces is called electrostatics.
1
rub
: apply steady pressure and friction to one
object/surface by moving another object/surface
repeatedly back and forth on it:
I rubbed my hands
together to get them warm
2
rug
: a small carpet often put on top of another one; a small
bedside/fireside carpet
3
damp
: slightly wet, humid
TEXT 3
Electrostatic Energy
KEY-WORD SEARCHING See
Reading strategies
on page 16
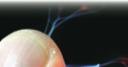
Spark from electric static jumping between two thumbs.
Progetto FOR ELECTRONICS_unit_1.indd 12
10/01/

