Basic HTML Version








3
Write the word
electricity
in the middle of the
blackboard and prepare a cluster with all the
words you know connected to electricity. Use a
dictionary if you need to.
4
Classwork
What is electricity? Write down a definition of electricity based on your previous
knowledge and compare it with those of your classmates, then write the best definition on the
blackboard.
5
Read the first two paragraphs and the conclusion of Text 1, and decide which of the following
could be considered main ideas.
a
The movement of charges
d
Electrical applications
b
Negative and positive polarities
e
Electrical characteristics
c
Electrons and protons
6
Skim the whole text and underline the main ideas. Then list them in the first column of the chart on
the next page and check whether your prediction was right.
2
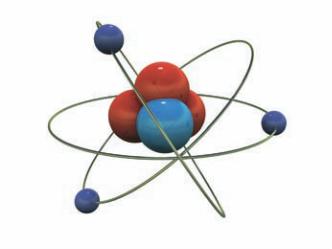
Look at this picture and describe what you see.
Inside an Atom
nucleus
orbit
electron
circuit
electricity
What is electricity?
E
lectricity is an invisible force that can produce
heat
, light, motion, and has many other physical
effects. The force is an attraction or repulsion between
electric charges. We see the effects of electricity in
batteries,
static charges
, lighting, radio, television,
and many other applications. But what do they all
have in common? They all have basic particles of
electric charge with opposite polarities. As you
probably know,
matter
(solids, liquids and gases) is
made up of
1
atoms containing two basic particles of
potential electric charges: electrons and protons.
Each atom consists of a central mass, called a
nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons and
electrons are arranged in rings or
shells
around the
outside of the nucleus. An electron is the smallest
amount of electric charge which has a characteristic
called negative polarity. A proton is a basic particle
TEXT 1
SKIMMING See
Reading strategies
on page 16
Progetto FOR ELECTRONICS_unit_1.indd 9
10/01/

